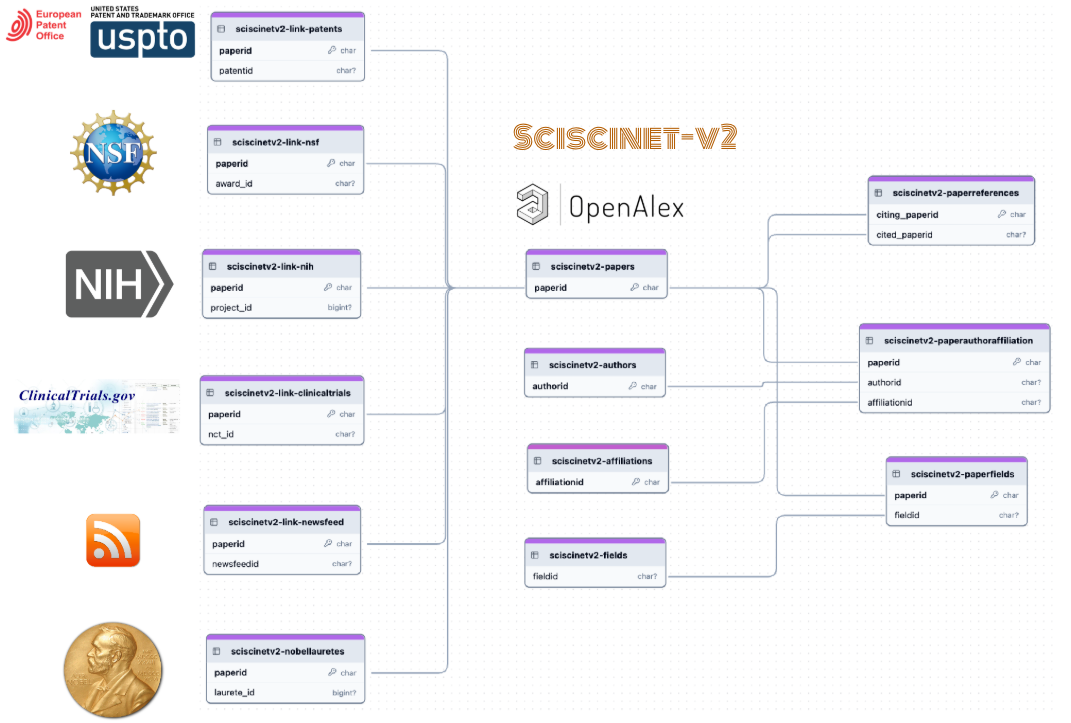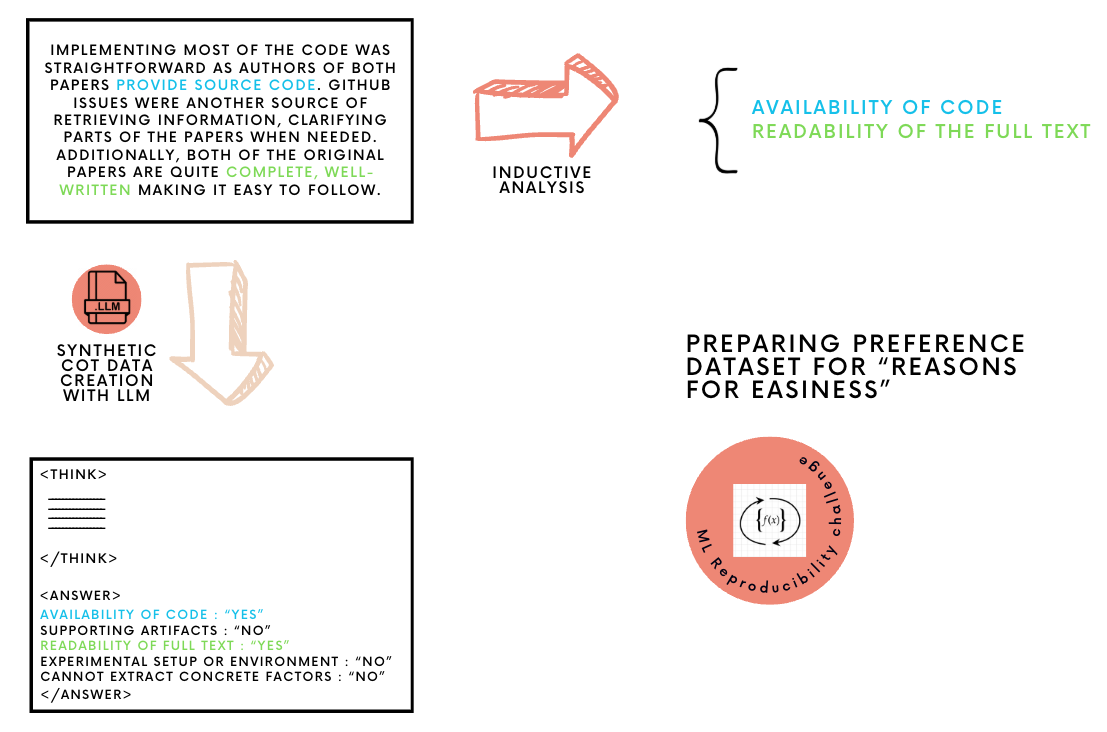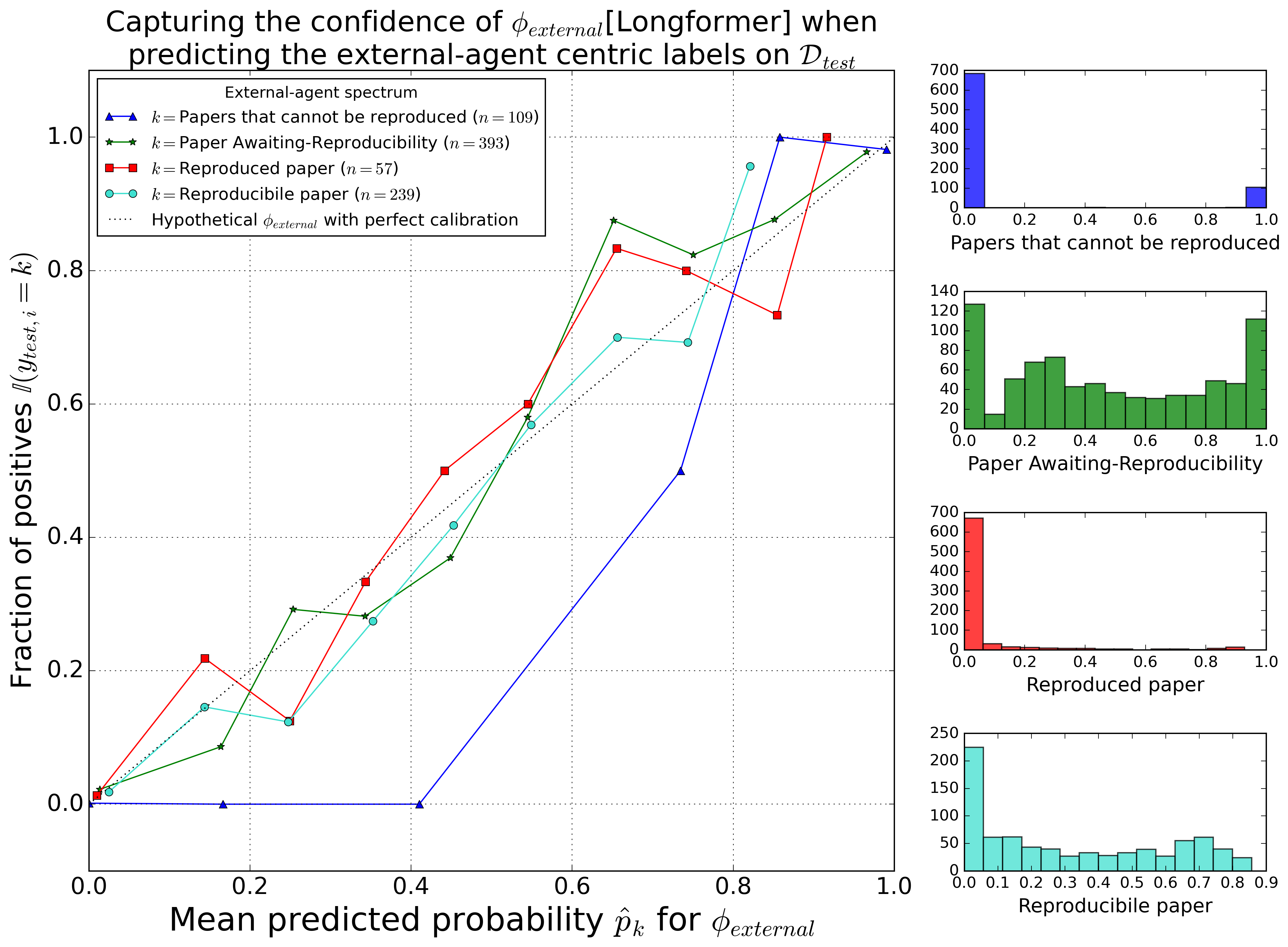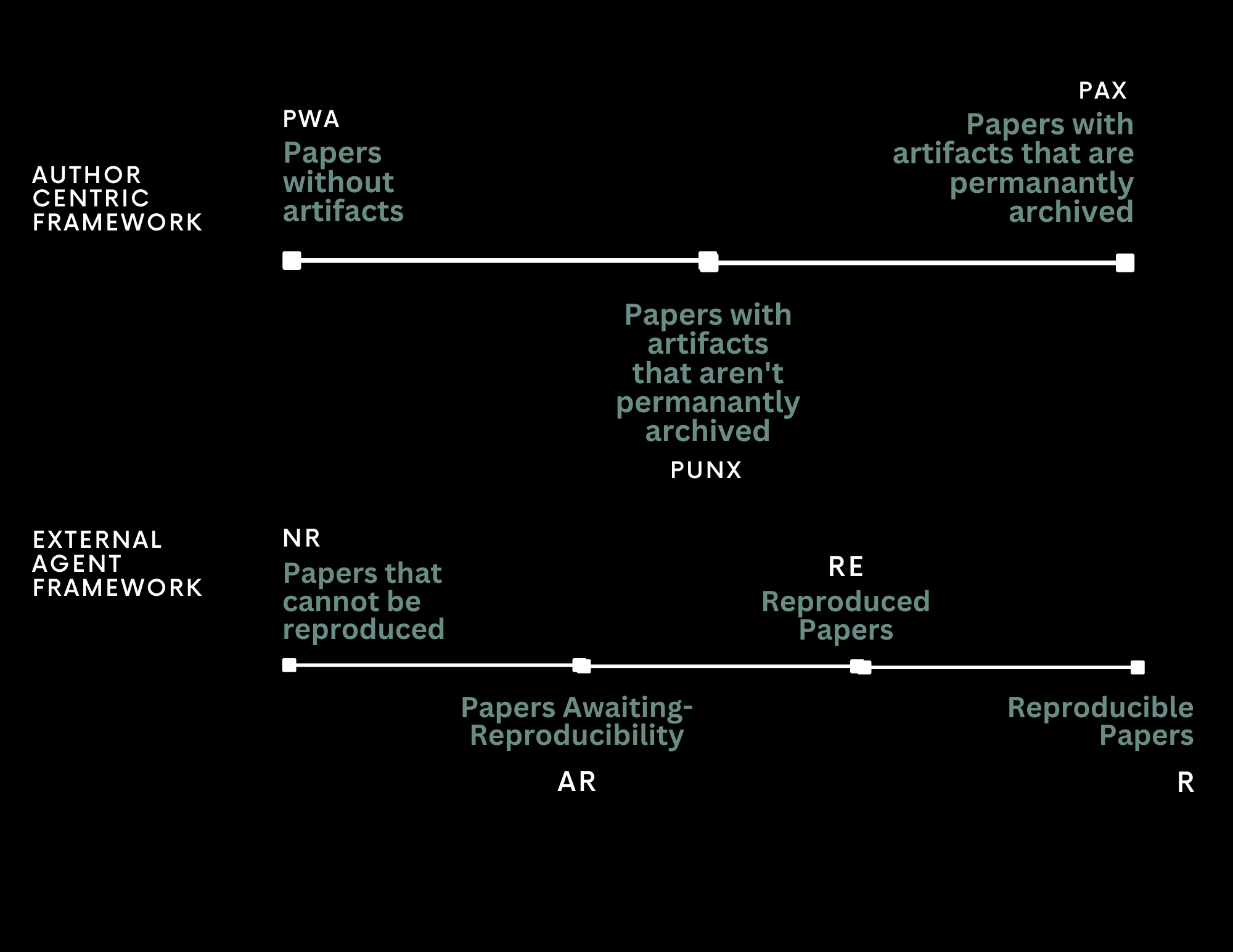
Pre-review to Peer review | Pitfalls of Automating Reviews using Large Language Models
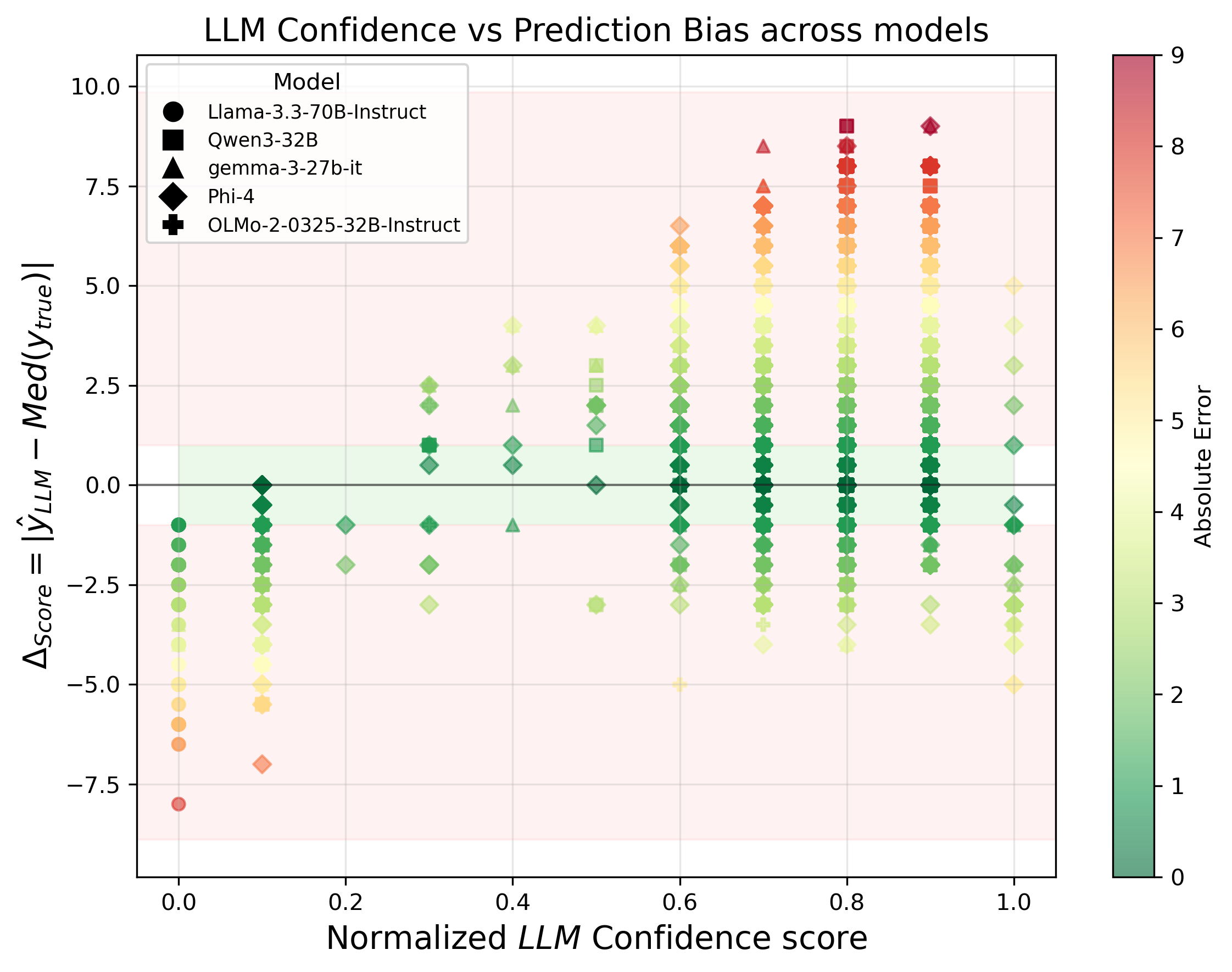
Abstract Large Language Models are versatile general-task solvers, and their capabilities can truly assist people with scholarly peer review as \textit{pre-review} agents, if not as fully autonomous \textit{peer-review} agents. While incredibly beneficial, automating academic peer-review, as a concept, raises concerns surrounding safety, research integrity, and the validity of the academic peer-review process. The majority of the studies performing a systematic evaluation of frontier LLMs generating reviews across science disciplines miss the mark on addressing the alignment/misalignment of reviews along with the utility of LLM generated reviews when compared against publication outcomes such as \textbf{Citations}, \textbf{Hit-papers}, \textbf{Novelty}, and \textbf{Disruption}. This paper presents an experimental study in which we gathered ground-truth reviewer ratings from OpenReview and used various frontier open-weight LLMs to generate reviews of papers to gauge the safety and reliability of incorporating LLMs into the scientific review pipeline. Our findings demonstrate the utility of frontier open-weight LLMs as pre-review screening agents despite highlighting fundamental misalignment risks when deployed as autonomous reviewers. Our results show that all models exhibit weak correlation with human peer reviewers (0.15), with systematic overestimation bias of 3-5 points and uniformly high confidence scores (8.0-9.0/10) despite prediction errors. However, we also observed that LLM reviews correlate more strongly with post-publication metrics than with human scores, suggesting potential utility as pre-review screening tools. Our findings highlight the potential and address the pitfalls of automating peer reviews with language models. We open-sourced our dataset $D_{LMRSD}$ to help the research community expand the safety framework of automating scientific reviews. ...