While technological and scientific advancement paved its way in the 20th century giving scope for researchers to publish of a plethora of scientific literature, “Public Understanding of Science” has been at the center stage of discussion among researchers for the past decade. This very concern sprouts from the fact that most of the scientific reportage that occurs on News Media is subject to personal interpretation. Also, the misapprehensions of the scientific findings can cause repercussions of unimaginable scale in the real world. Let us consider a small use case. For suppose, “ABC” is a research organization that publishes a scientific finding regarding the relationship between pregnancy and theobromine. Now, there might be a news media outlet that picks the same research article and broadcasts the results in a science journalism segment. The problem arises if the findings in the research paper are incorrectly represented by the Media Outlets. If the research finding says “There is a 30% chance of not having a miscarriage during pregnancy if the woman has theobromine in her diet”, the media outlet would report it in the following way, “A recent finding suggests that chocolate is good for your health during pregnancy and it would help you to reduce the chance of a miscarriage”.
Questions I am trying to answer ?
The scientific literature when shared on diverse digital platforms has repercussions on a larger scale as it is subject to diverse public perception. The study mainly aims to assess and understand the meaning conveyed about scientific literature to general public and what are the effects of such opinions in the real world.
Goals
The core aim of the study is to mathematically frame the effects of public understanding about scientific literature on real world. Effects here implies psycometric and economic. The study would therefore be divided into two phases. Phase 1 would involve predicting the level of public perception (understanding) of scientific articles purely basing on the text from the abstract. Phase 2 would broadly focus on coming up with economic and psycometric effects of public understanding about scientific literature on real world.
Results and findings
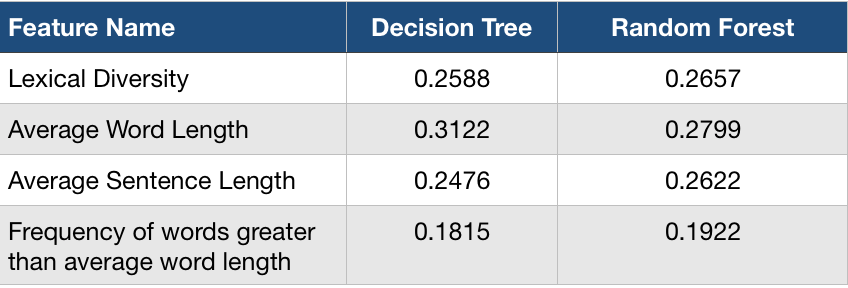
For proving the hypothesis I tried creating a machine learning module that would predict the level of understanding of scientific articles purely based on the text present in the abstract. Regression was used to predict the level of understanding and for the module and here are the following features that were considered during the process of the regression :
- Average word length
- Average sentence length
- Lexical Diversity
- Frequency of words greater than the average word length
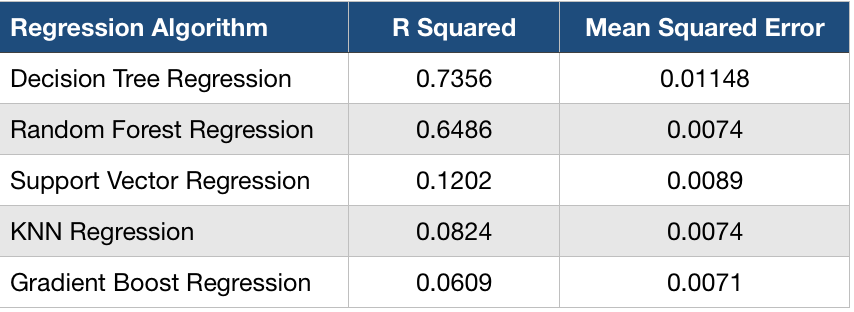
MSE stands for “Mean Squared Error” which is nothing but the difference between the estimator and what is estimated. R2 stands for “R-Squared” value which is nothing but the statistical measure of how close the data are to the fitted regression line. It ranges from 0 to 1. If the value is 0 it would mean that the model explains none of the variability of the response data around its mean. If the value is 1 then it indicates that the model explains all the variability of the response data around its mean. The model that I have built has an R-Squared value of 0.7356.
Future Work
The future work would focus on mathematically hypothesizing a relationship between the proposed psycometric and economic effects of public understanding about scientific literature. There must be active research done towards constructing and understanding the relationship between the afore mentioned variables. Furthermore, an in depth understanding about the ripples caused by news media articles on the economy would the primary priority whilst understanding the psycometric effects of the news media articles would be the second priority.
Github Repository: pubundsci
Thats it folks, Happy Hacking !!